In the rigorous domain of warehouse operations, robust quality control is indispensable for safeguarding product integrity through meticulous inspection, quarantine, and traceability measures. 3PL professionals often contend with issues like inconsistent sampling during incoming goods checks and fragmented documentation, which can compromise shelf-life management and slow recalls. In practice, a WMS should complement, not replace, technical quality functions by capturing the data points that operations teams and quality teams already measure, then making that data easy to search and act on.
Conventionally, establishing comprehensive quality control required prolonged manual audits and paper trails to address non-conformances under ISO 9001. A modern WMS speeds this up by recording batch, date and quantity at receipt and by linking those attributes to tasks and transactions so that teams can immediately see what shipped, what is allocated and what is still in stock, and can place affected stock on hold within seconds when a recall notice lands.
This article dissects common pitfalls and explains how a configurable WMS supports quality control with accurate data capture, GS1-based traceability and clear audit trails. It also adds expert commentary drawn from front-line warehousing practice.
What is Incoming Inspection and How Do I Optimise It?
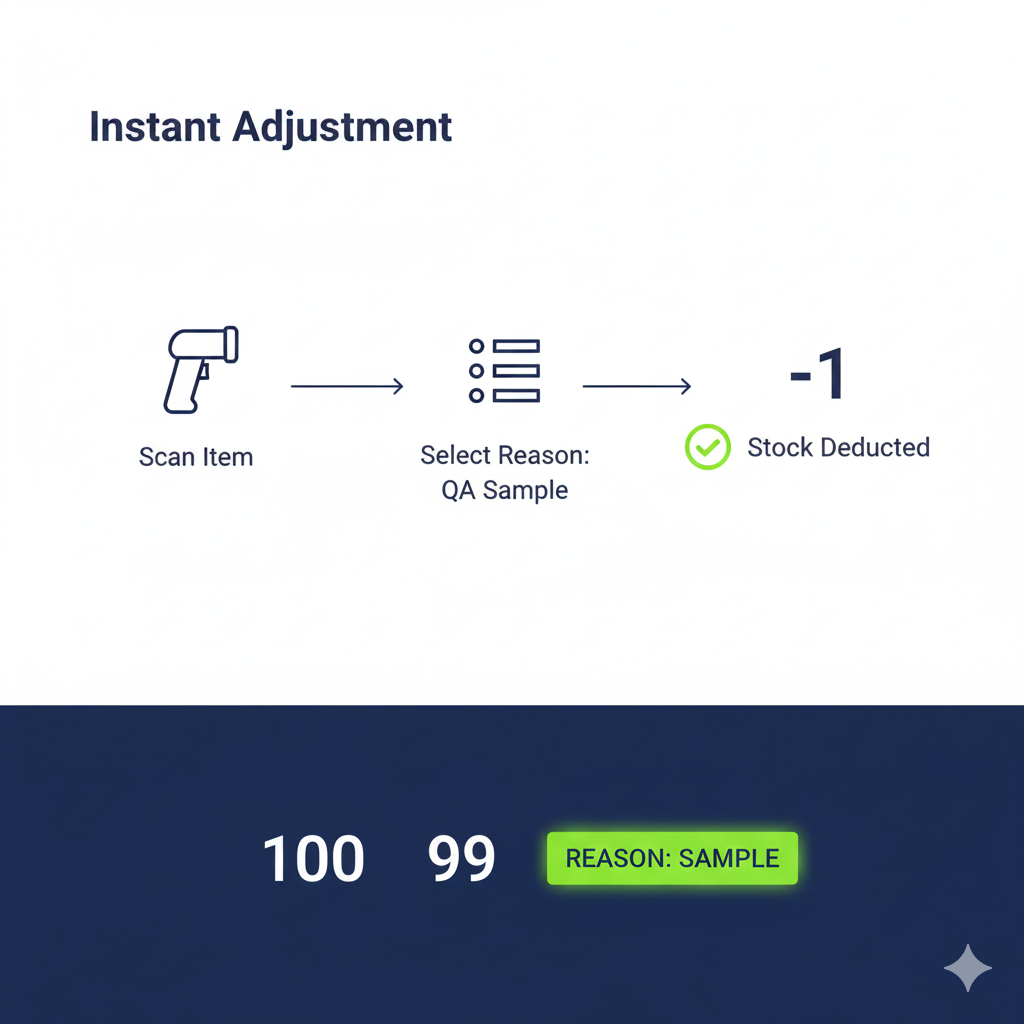
Incoming inspection validates supplier quality using defined acceptance criteria and sampling, and it drives decisions about quarantine and onward processing. In many operations, Acceptance Quality Level (AQL) plans are owned by the quality team, not the WMS. The WMS’ job is to record what was sampled and adjust on-hand quantities accordingly, for example deducting 5 kg taken for testing from a 1,000 kg receipt, and to timestamp who did the check and when.
Expert insight: “All we need to track is that something has been taken for sampling, and you can amend the stock that you’ve taken for sampling because that sample is not coming back.”
Practical tip: Use GS1 barcodes and application identifiers where available to scan product code, batch, expiry and quantity at the dock, which reduces typing and errors compared with manual entry.
How Do Storage Conditions Impact Quality Control?
Storage conditions, such as temperature and humidity, determine product integrity and shelf life. In regulated environments like pharmaceuticals, Good Distribution Practice (GDP) expects appropriate storage conditions, alarm management and documented actions when excursions occur. A WMS can capture the measured values as attributes and link them to receipts or picks, but specialist temperature mapping and continuous monitoring procedures normally sit with the quality function.
Expert insight: If your process requires capturing a temperature at receipt, you can prompt the handheld flow for a reading and store it on the transaction, but full temperature mapping and chamber monitoring are quality processes outside the WMS.
External guidance: See MHRA GDP guidance and the EU GDP guideline for expectations on storage, monitoring and deviations.
Do I Need Traceability for My Warehouse Operations?
Yes. End-to-end traceability enables both backward and forward searches during incidents. Using GS1 Serial Shipping Container Codes (SSCC) on pallets and cases allows a single scan to identify a logistic unit and link it to its contents, batches and dates, which improves speed and accuracy on inbound and outbound. When suppliers pre-advise pallet data and you are GS1-compliant, receipt can be reduced to a single pallet-label scan to confirm arrival.
Expert insight: “If your supplier is GS1-compliant and sends the data in advance, you can reduce your receipt process to one scan of the pallet label.”

What Role Does HACCP Play in Food Warehouses?
HACCP sets the framework for identifying hazards and establishing Critical Control Points in food storage and distribution. In a warehouse, this often includes pest-control checks, segregation rules and temperature control where applicable. The WMS supports HACCP by prompting the right checks for the right products in the handheld flow, recording who performed them and when, then exposing that evidence in reports or interfaces.
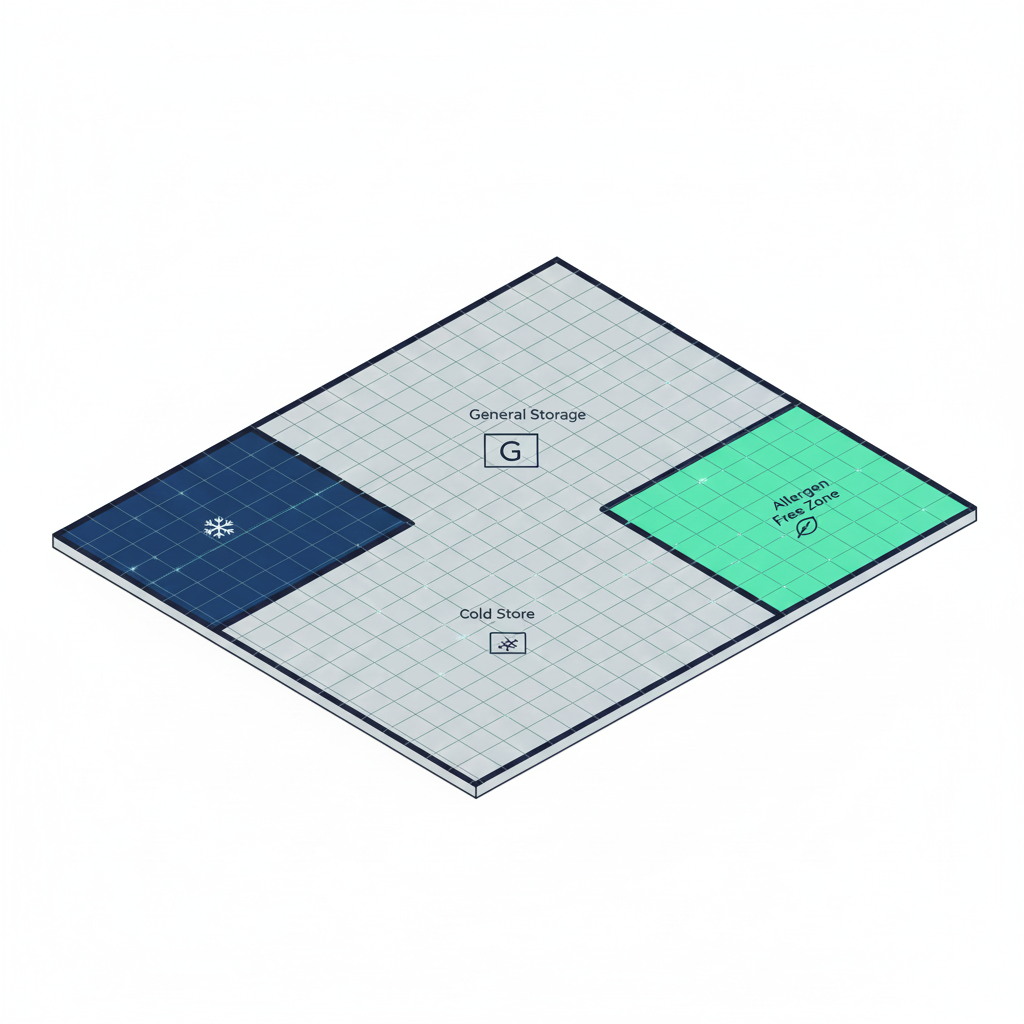
Expert insight: Use predefined location groups to segregate allergens or gluten-free products so that putaway suggestions never propose a location that risks cross-contamination.
Traditional Methods vs. a Configurable WMS for Quality Control
Where manual methods struggle
- Manual keying of product, batch, date and quantity at receipt is time-consuming and error-prone.
- Paper-based hold and release processes slow down recalls and reallocation.
What a WMS should handle
- Scan-to-capture of GS1 Application Identifiers to pre-populate product, batch, expiry and quantity.
- Quick stock holds and batch reallocation to stop non-conforming goods shipping.
- Switch-by-scan when FIFO allocation selects an inaccessible pallet in bulk stacks.
Why Teams Struggle with Quality Control
- Disjointed systems: quality checks recorded outside the WMS are hard to search during audits.
- Manual data entry: non-GS1 receipts require repeated typing of key attributes.
- Physical constraints: FIFO in bulk-stacked lanes often clashes with accessibility, which requires controlled switching.
How Does Clarus WMS Handle Quality Control?
Clarus WMS focuses on operational data capture and control. It provides configurable handheld flows to prompt checks, timestamps every action, and integrates GS1 scanning so product, batch, date and quantity flow through receipts, picks and dispatches with minimal typing. It also supports rapid quarantine by letting supervisors put stock on hold immediately and by showing what shipped, what is allocated and what remains in stock for a given batch.
Configurable Automations
Automations can trigger actions on events, for example sending an ASN file when an order completes, or selecting a carrier based on address and weight rules. These are expanding and can be combined with handheld configuration to drive the right work at the right time.
Traceability and Rapid Recall
By capturing product, batch and date at inbound and linking them to tasks and shipments, the system enables fast backward and forward tracing. Teams can reallocate picks off a bad batch, hold the remainder and extract shipment lists to contact customers.
What Clarus WMS Does Not Do
- AQL sampling design: acceptance sampling plans are owned by the quality function. The WMS records that a sample was taken and adjusts quantity.
- Temperature mapping: chamber mapping and continuous monitoring are quality processes. The WMS can capture readings but does not perform mapping.
References
“Getting warehouse automation right,” McKinsey
“Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC),” GS1
“GS1 Application Identifiers,” GS1
“Medicines: Good manufacturing practice and good distribution practice,” MHRA
“EU Guidelines on Good Distribution Practice (2013/C 343/01),” European Commission
“Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP),” Food Standards Agency

